This post lists the basic things to check when a user says they can’t access the internet, and some potential fixes. Note this is aimed at small networks without proxy servers or standalone firewalls, as those systems can add additional filtering and troueblshooting steps.
1 – Reboot the Router
On a small network then there is not a lot to be lost by rebooting the internet router. Occasionally it can cause the speed to drop temporarily, other times it can speed things up. Most routers have an internet light which is lit green when the router is logged into the internet. Note there is a difference between an ADSL line being connected physically and the internet being logged in. For example if the ISP bill hasn’t been paid then the account just might be blocked from signing in.
2 – Phone up the ISP ( Internet service provider )
They should be able to check the link back to the router and advise if they think there is a fault or it’s working.
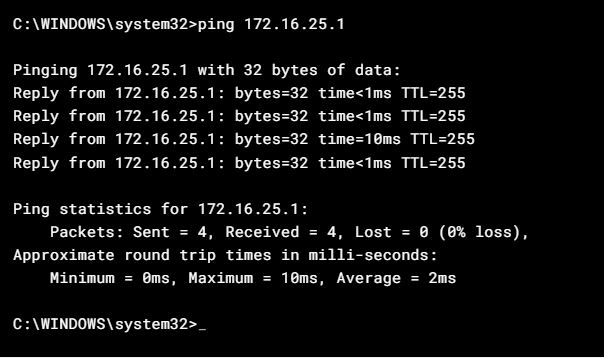
3 – Can a PC ping the router.
Most routers respond to internal PING requests ( sometimes it’s blocked, so best to check this when everything is up and working first ). To find the routers IP address open up a CMD window and type in IPCONFIG
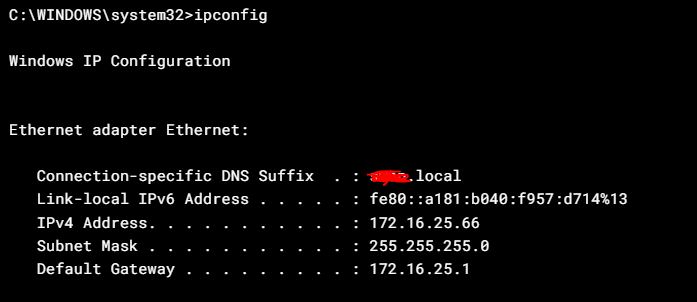
The default gateway is the routers IP address. If you ping that address you should get a reply. it’s worth noting that if the link ( eg cable, wifi ) to the router isn’t working then you might see an address that starts “169 …” if you see this that is a pretty good indication that the PC can’t find anything to give it an IP address ( usually the router on a small network ), so time to go troubleshoot the physical connection.
If you can ping the router ok, then thats a good sign that the internet network is ok ( including PC network adapters, cable, wifi, routers local network ).
4- Ping an external IP address
If you can an external IP address by putting in the actual address, then you are testing connectivity before DNS is used. If you open up a CMD window and type in PING 8.8.8.8 you are pinging a Google name server, which usually responds. If this doesn’t respond then there is likely a problem with the internet link so time to get in touch with the ISP.
5 – Ping a site by it’s Domain Name.
If step 4 works, then time to check the domain name resolution ( DNS ). Sometimes DNS servers fail, and a possible resolution is to try to change the PC’s DNS server away from it’s default ( usually the router ) to something like Google ( 8.8.8.8 ). Here’s an example of a ping working to www.bbc.co.uk, which implies that the internet link is up, and DNS is resolving ok.
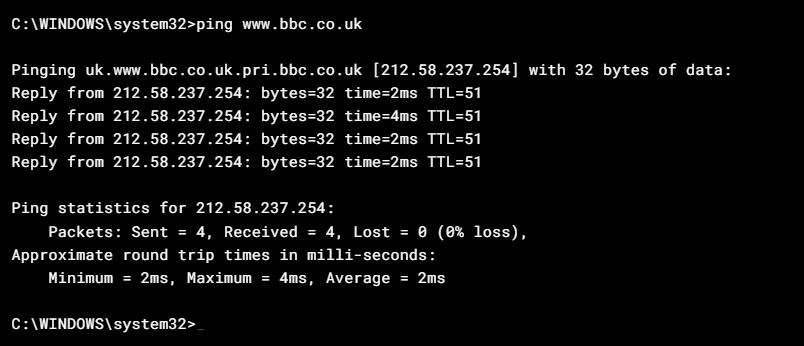
If this ping does work, but there are still issues accessing web sites or email, then one thing that we have seen is that with BT lines if a bill hasn’t been paid then pings can still work. and even the opening google search page opens, but anything else just times out. So again speak to your service provider.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.